Anatomy and Structure of Human Mouth and Teeth
Good knowledge of the morphology, anatomy, structure and physical characteristics of mouth and teeth is necessary in order to understand the development of several dental conditions, their causes and their treatments.
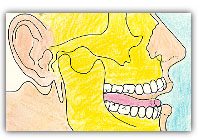
Human Mouth, also known as Oral or Buccal Cavity, is a complex body structure that consists of both hard and soft dental and periodontal tissues.
Read more »
Mouth Functions include mastication (chewing of food), tasting foods, formation of speech, and contributing to facial appearance and expressions.
Read more »
The main Parts of a Tooth are the Crown that is the visible part of the tooth and the Root, the part under the gums that anchors the tooth.
Read more »
Teeth Names & Numbers used to distinguish specific teeth are based on several teeth numbering systems such as the Universal system used in US.
Read more »
Baby Teeth, also known as primary, milk or deciduous teeth, are the first set of human teeth that will be replaced later by the permanent teeth.
Read more »
Parts of the mouth anatomy include the teeth and gums, lips and cheeks, jaws, tongue, palate, salivary glands, floor and muscles of the mouth.
Read more »
The 4 Types of Human Teeth are incisors, canines, premolars and molars, each with different shape, morphology and function.
Read more »
The internal Tooth Anatomy consists of 4 different tissues: enamel and cementum as outer layer, dentin, and dental pulp in the center.
Read more »
Tooth formation and development begins from the sixth week of pregnancy with most baby teeth partially formed in the jaw by the day of birth.
Read more »
Permanent teeth are the set of 32 teeth (secondary or adult teeth) that we get after the age of 6 yrs and serve us for the rest of our lives.
Read more »

